资料下载
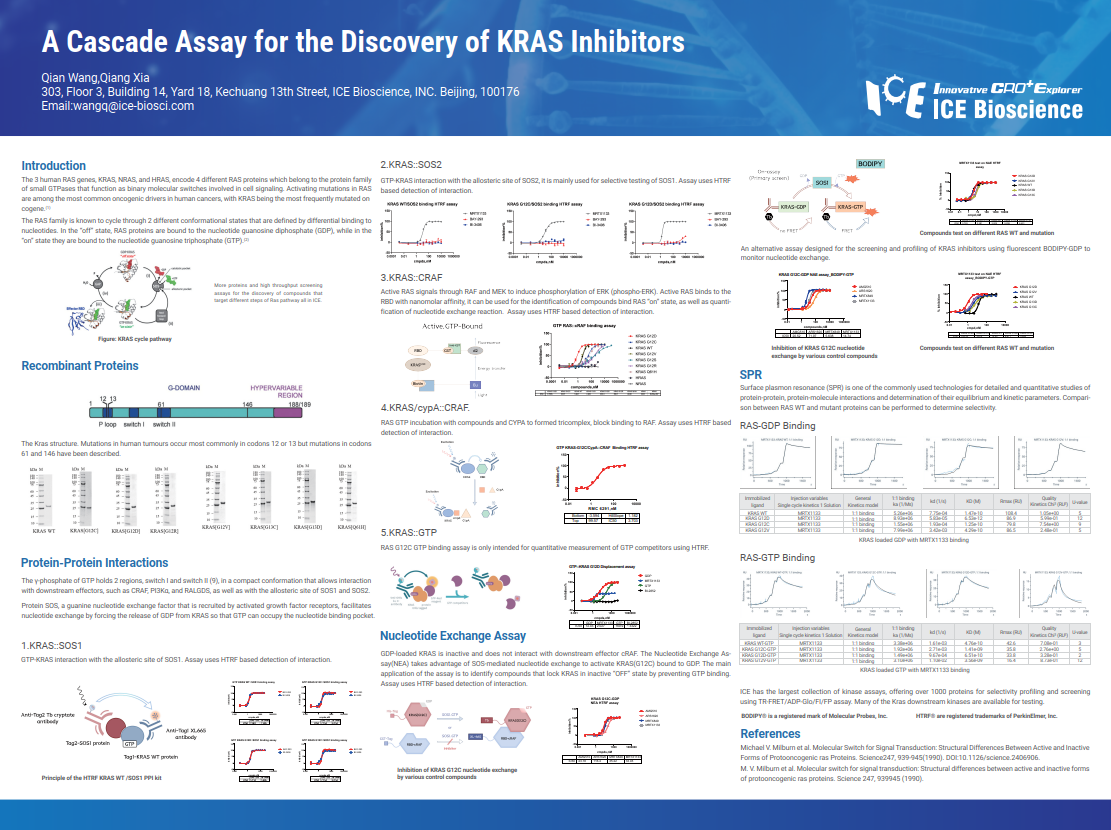
The 3 human RAS genes, KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS, encode 4 different RAS proteins which belong to the protein family of small GTPases that function as binary molecular switches involved in cell signaling. Activating mutations in RAS are among the most common oncogenic drivers in human cancers, with KRAS being the most frequently mutated oncogene. The RAS family is known to cycle through 2 different conformational states that are defined by differential binding to nucleotides. In the "off" state, RAS proteins are bound to the nucleotide guanosine diphosphate (GDP), while in the "on" state they are bound to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP).